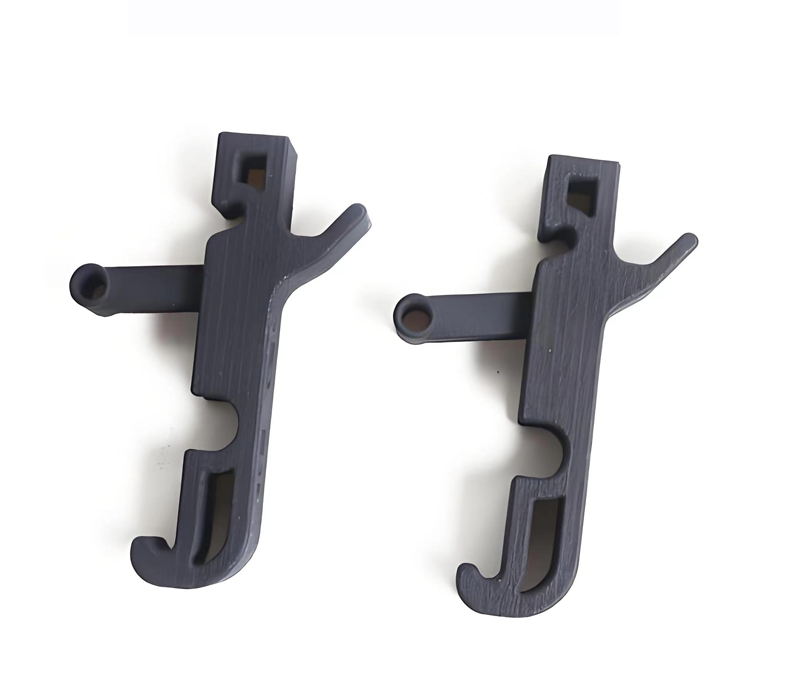
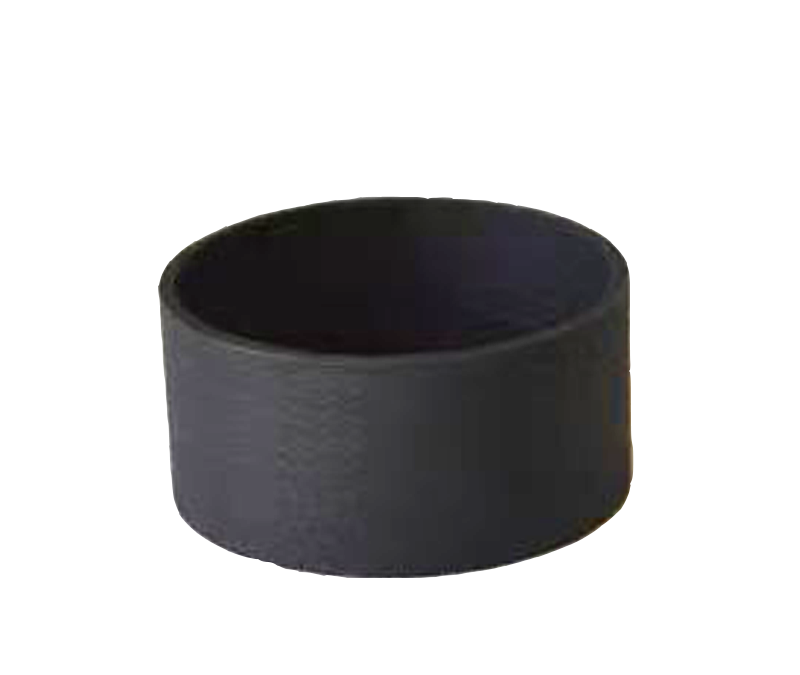
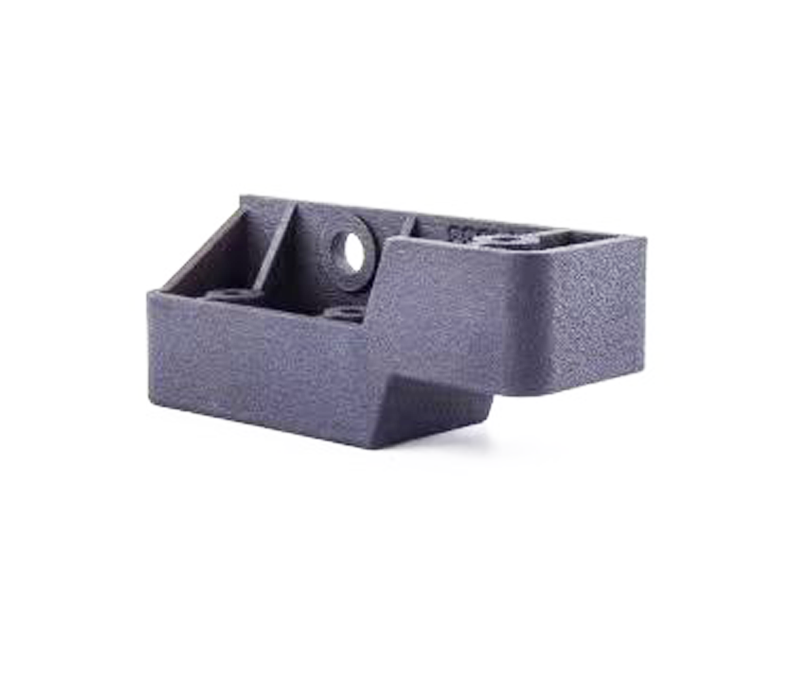
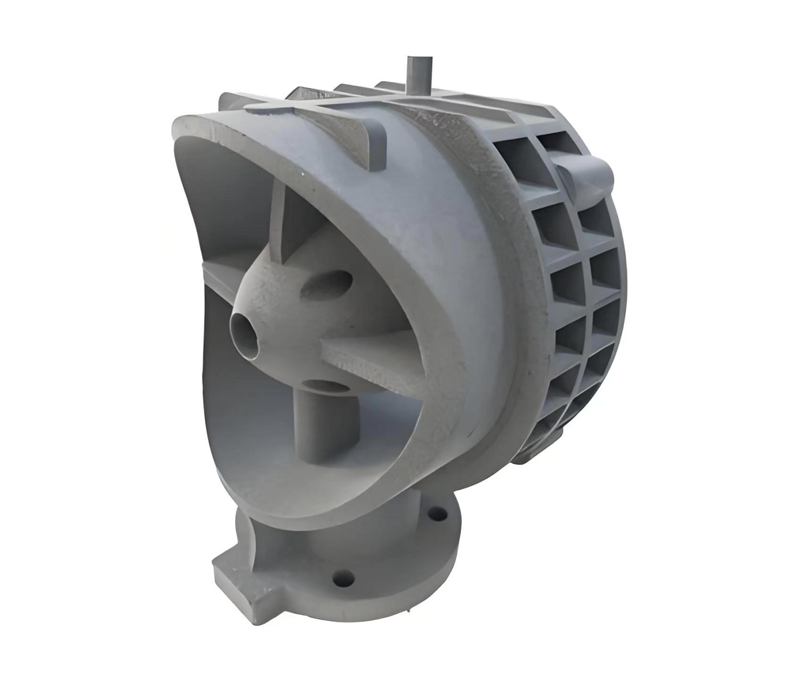
ARapidPrototype
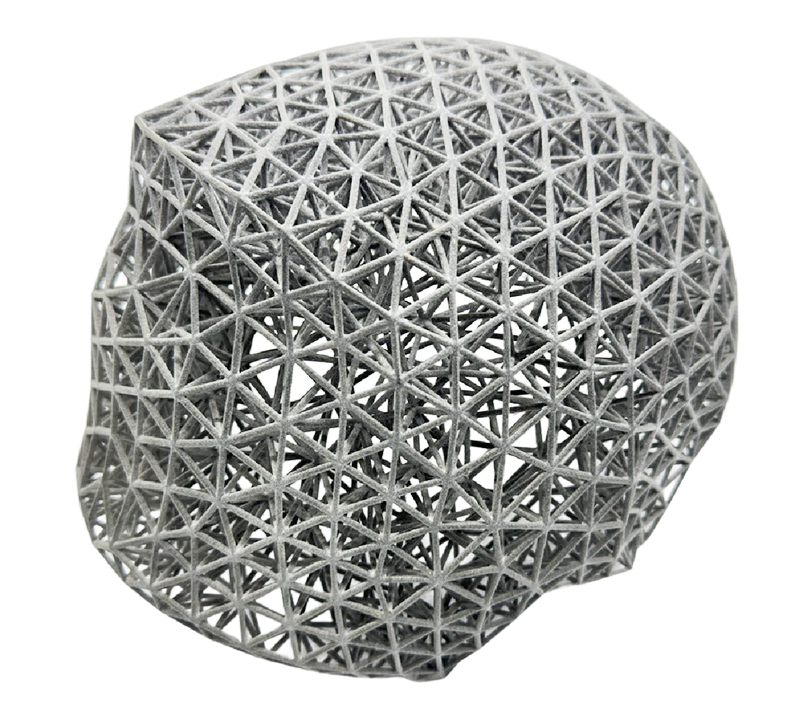
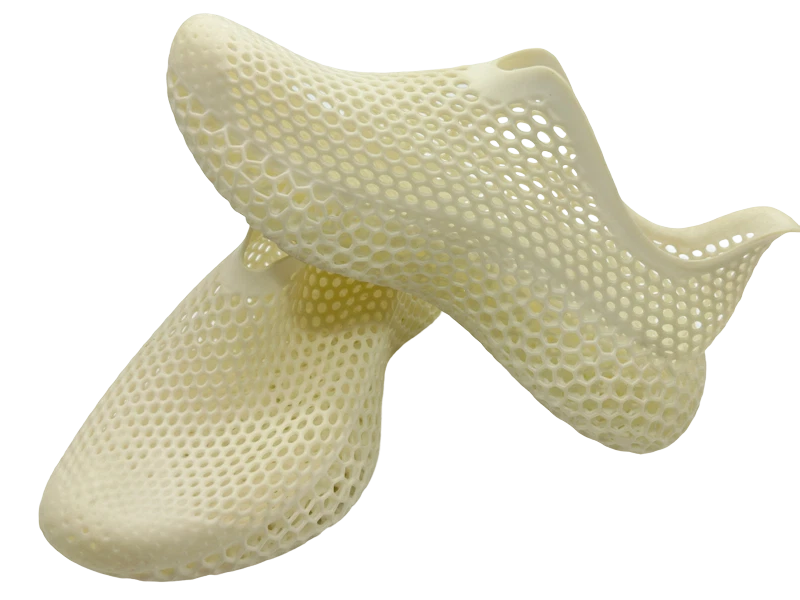
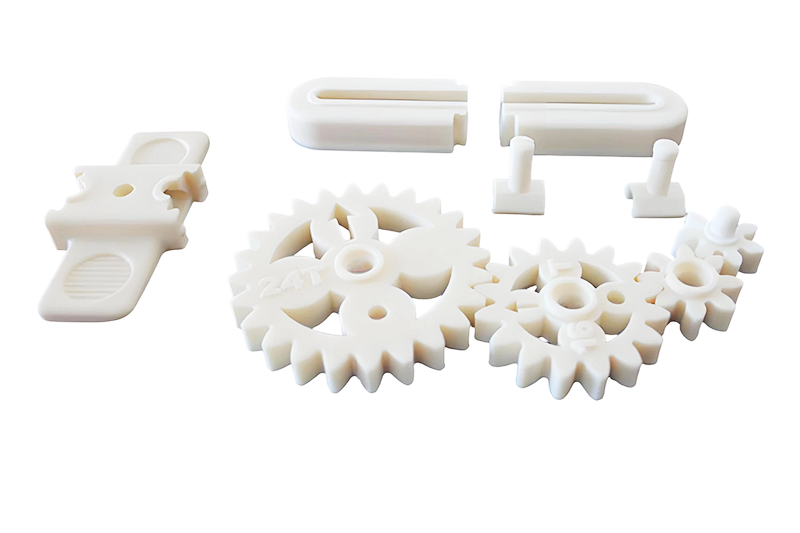
SLS 3D Printing Services
- Choose from a variety of industrial-grade materials and extensive surface finish options.
- Enjoy a standard lead time of just 3 business days for rapid delivery.
- Ideal for producing jigs, fixtures, housings, snap fits, and living hinges